Overview
Overview and modelling of the basic schema.
Data specifications and data schemas
Data specification denotes a set of similar data schemas, usually describing one thing differently or using different data formats. Data schema belongs to a data specification and models concrete data schemas, such as CSV schema or XML schema. Data schema may describe multiple data formats if you do not require advanced constructs for the given format. You can consider data specification as a project having multiple schemas.
An example of data specification and data schemas may be, for example, one of the following:
- specification: Tourist destinations
- schema: XML format
- schema: JSON format
- specification: Tourist destinations
- schema: for XML and JSON format
- specification: Tourist destinations
- schema: XML for old information system
- schema: XML for new information system
Schema for Tourist destinations
Start in the specification manager by creating a new data specification.

In the specification detail, create a new data schema, which will redirect you to the schema editor.
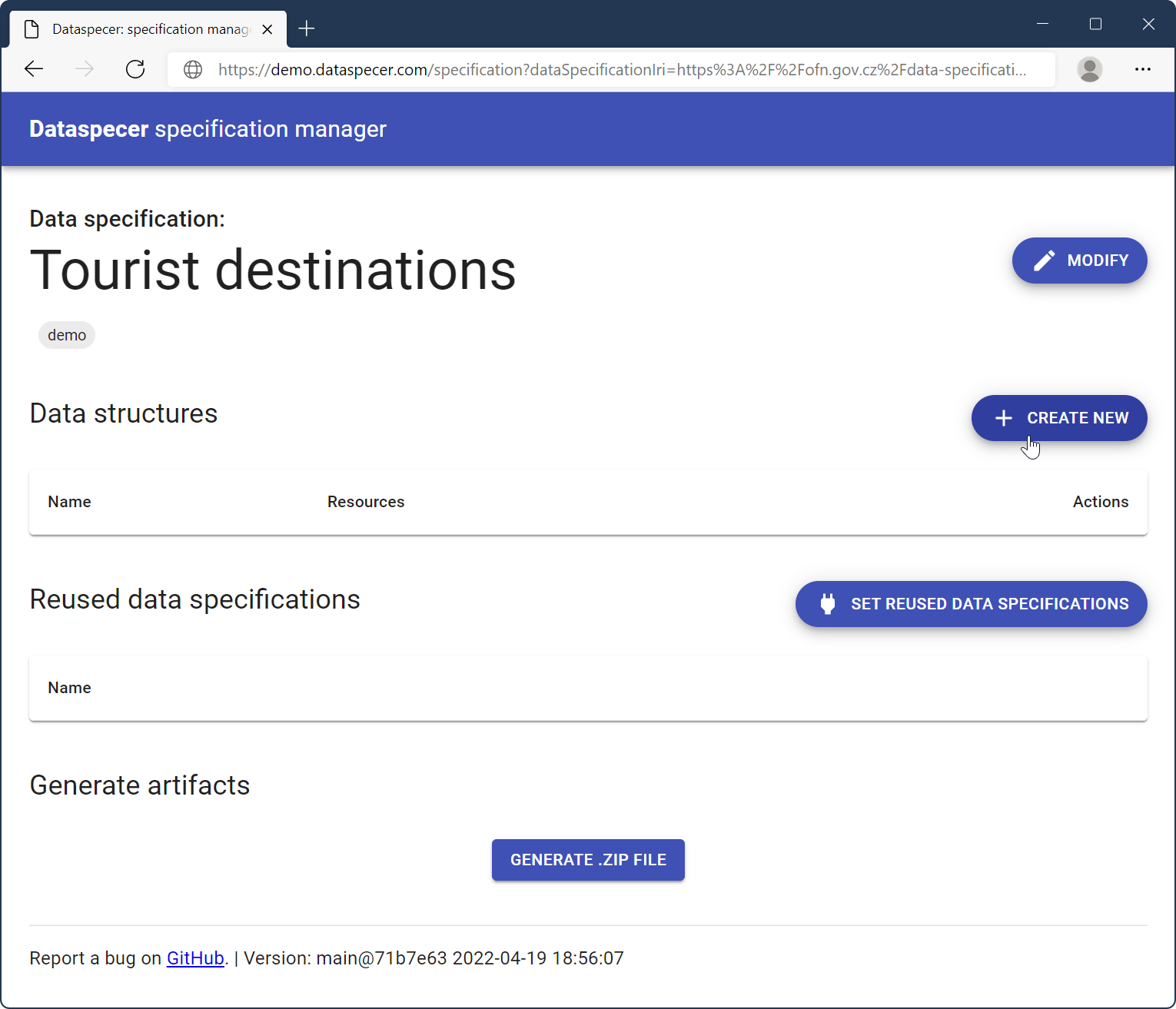
Start by selecting a root class from the search box. The chosen class became the root of your given schema. From that root, you will be able to add attributes and associations to other classes.
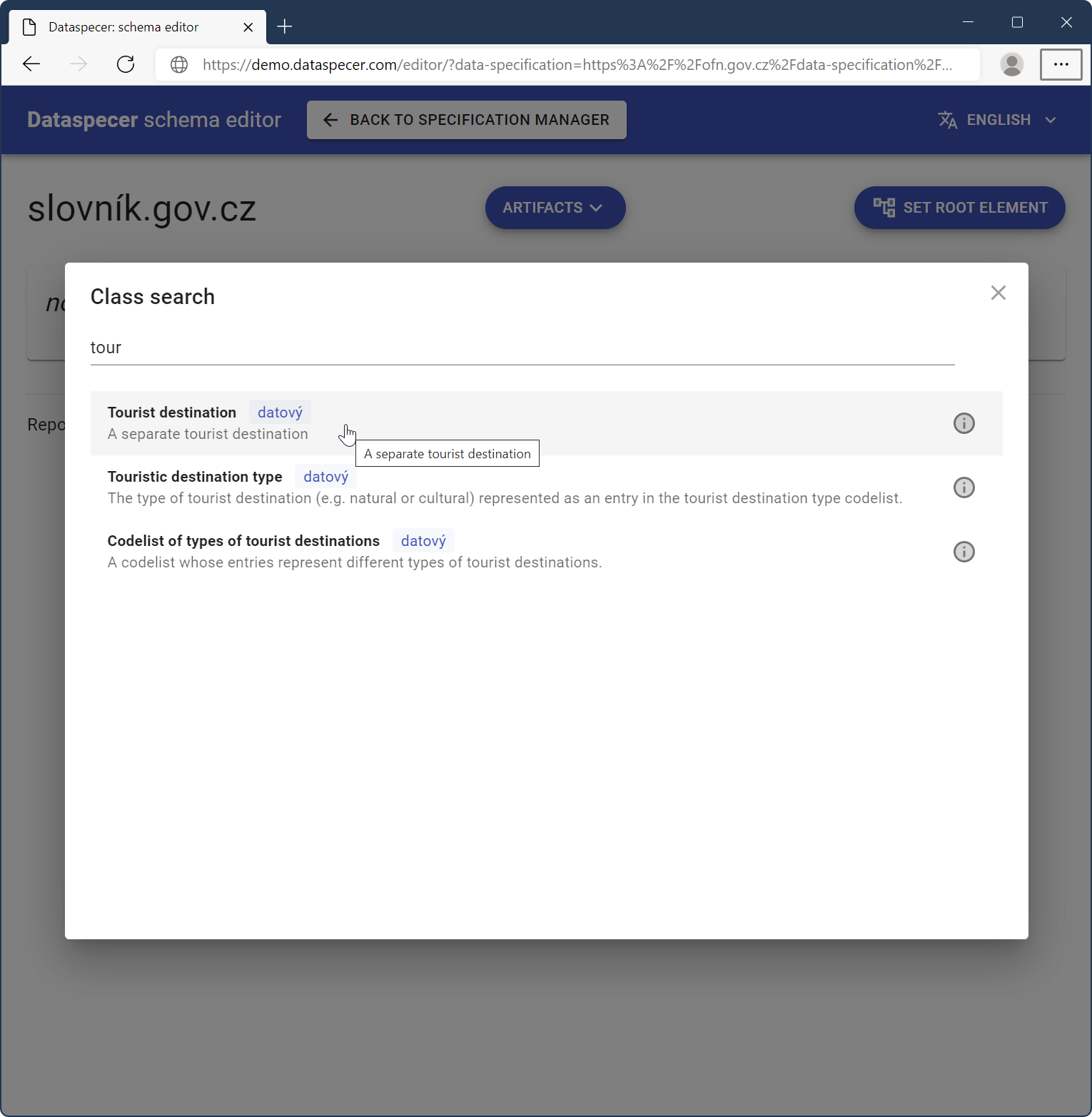
On the main screen, you can see the class added.
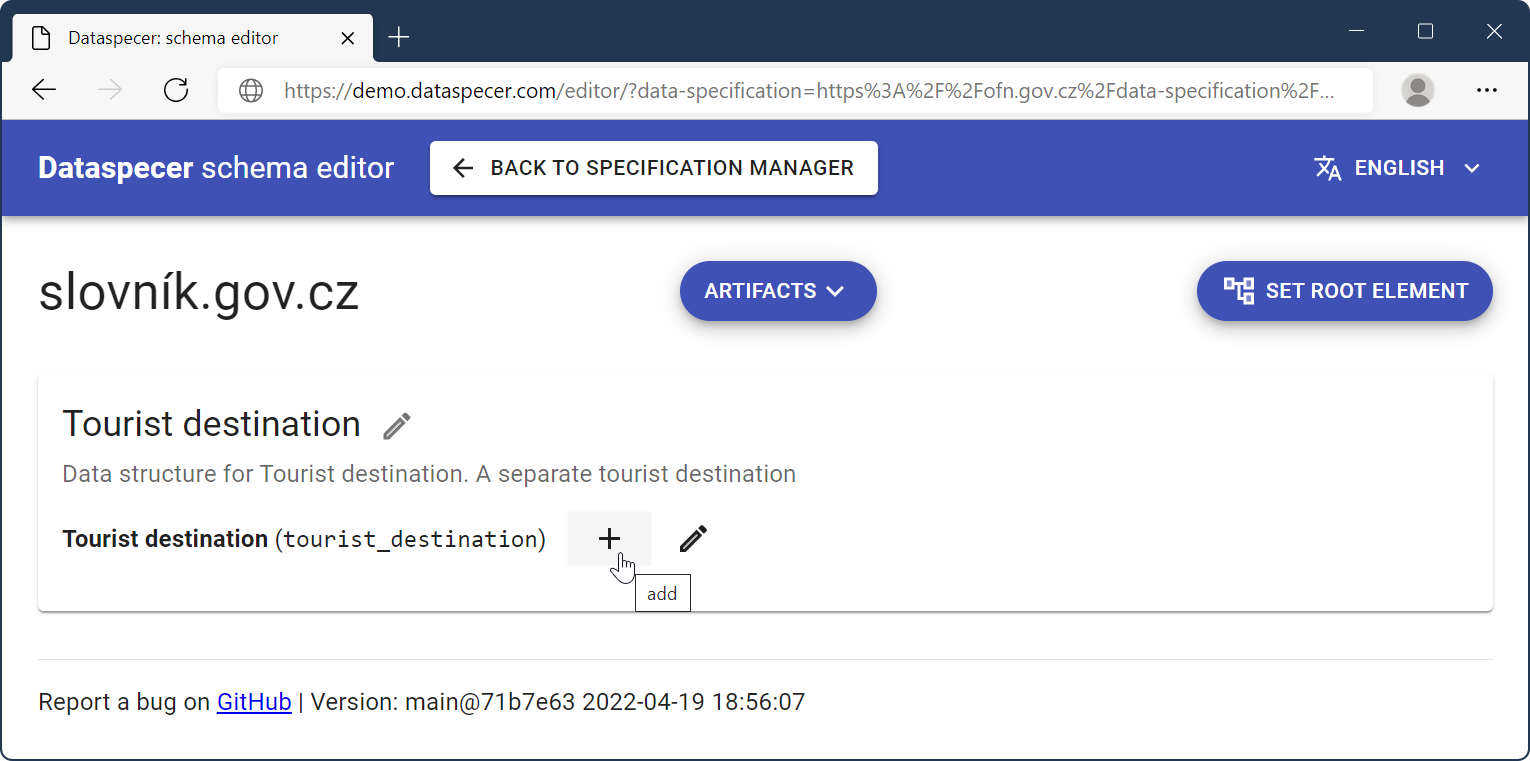 By clicking on the plus icon next to it, you can add attributes and associations that belong to the class. On the left side, you can switch to ancestor classes of that class and add attributes and associations from it.
By clicking on the plus icon next to it, you can add attributes and associations that belong to the class. On the left side, you can switch to ancestor classes of that class and add attributes and associations from it.
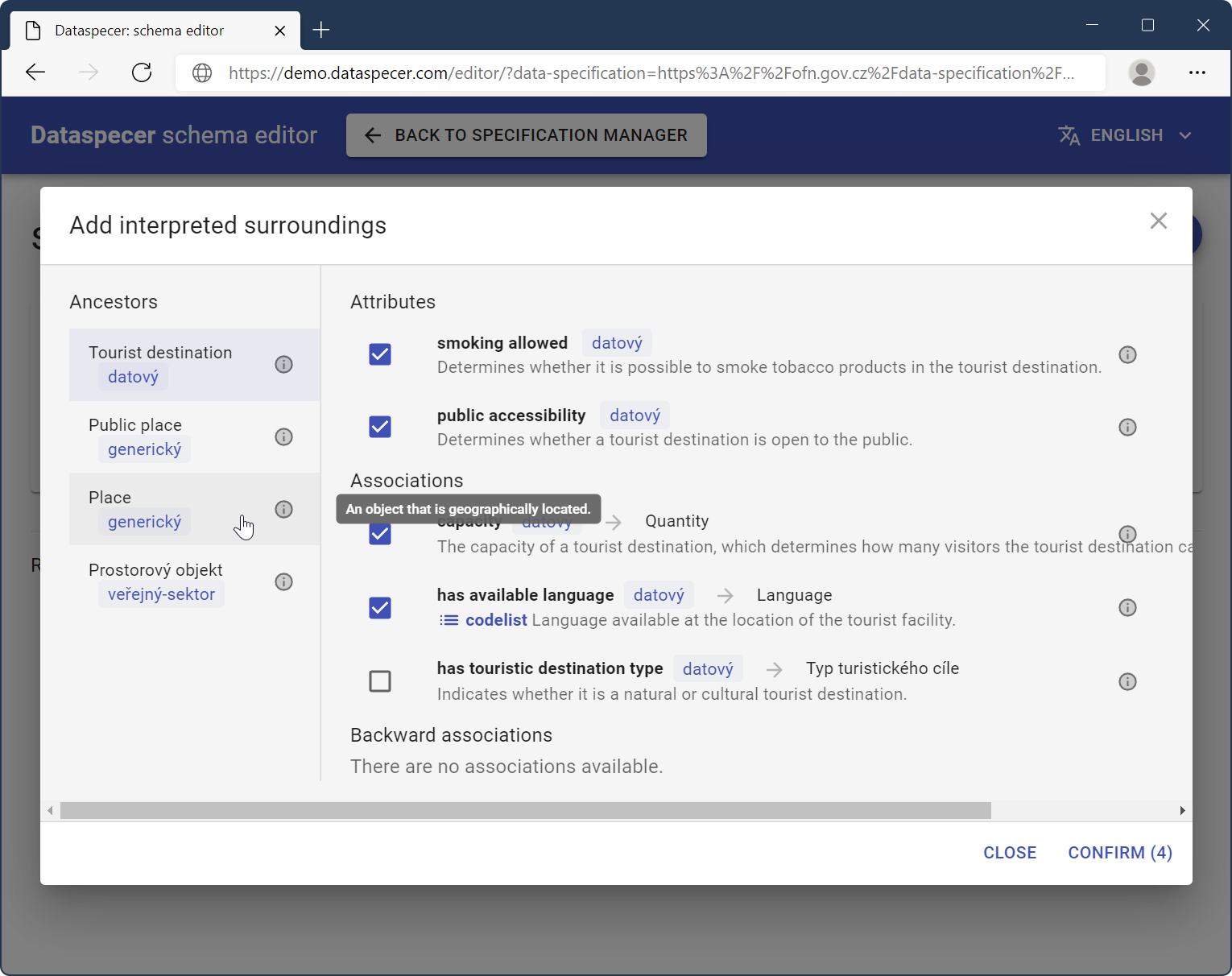
You may reorder the list of attributes and associations, rename their labels or remove them. Any advanced operation can be performed through the dialog, which is accessible from the menu, similar to the “+” button next to classes.
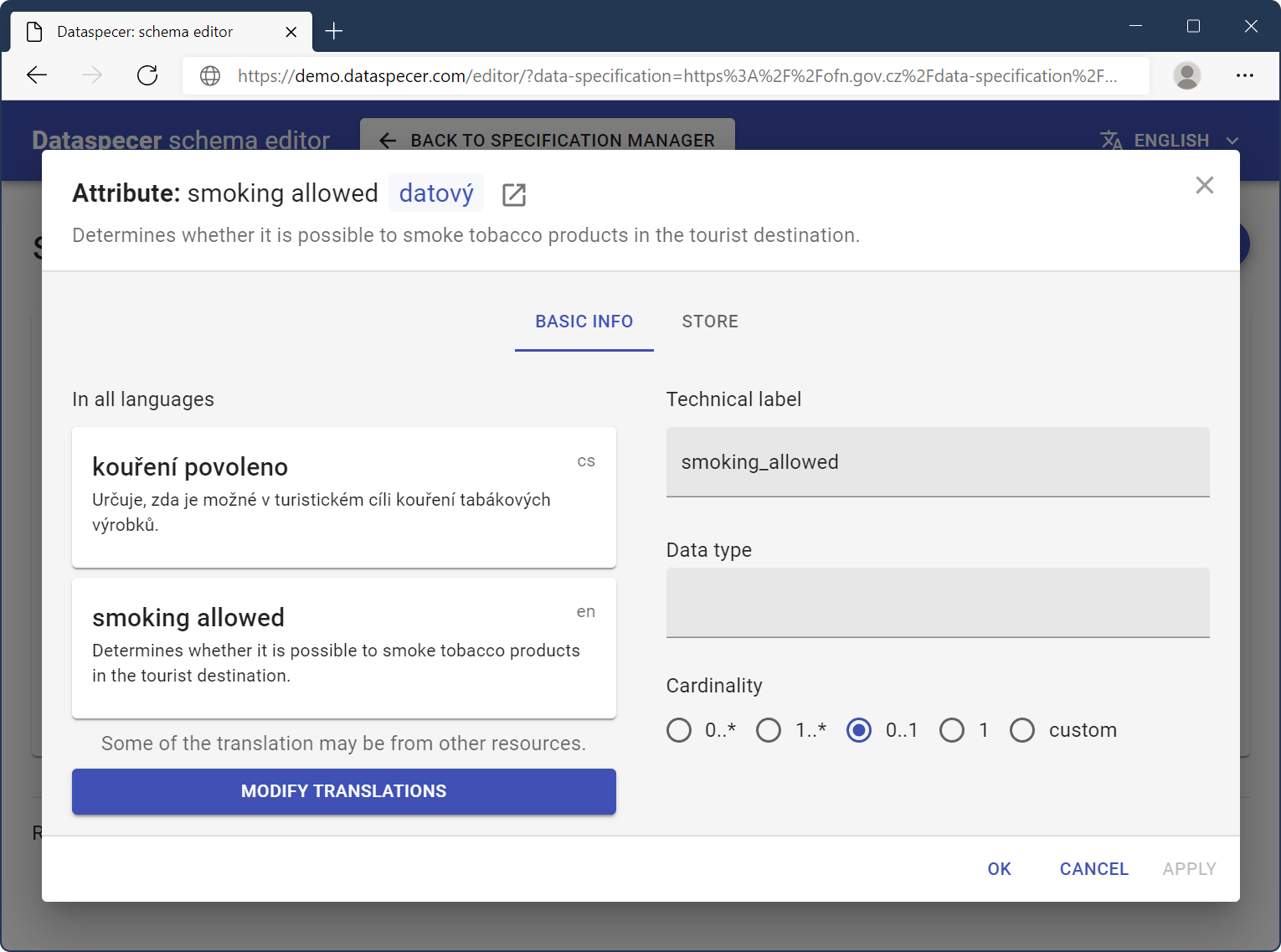
You can go deeper by extending the child classes in an equivalent manner.
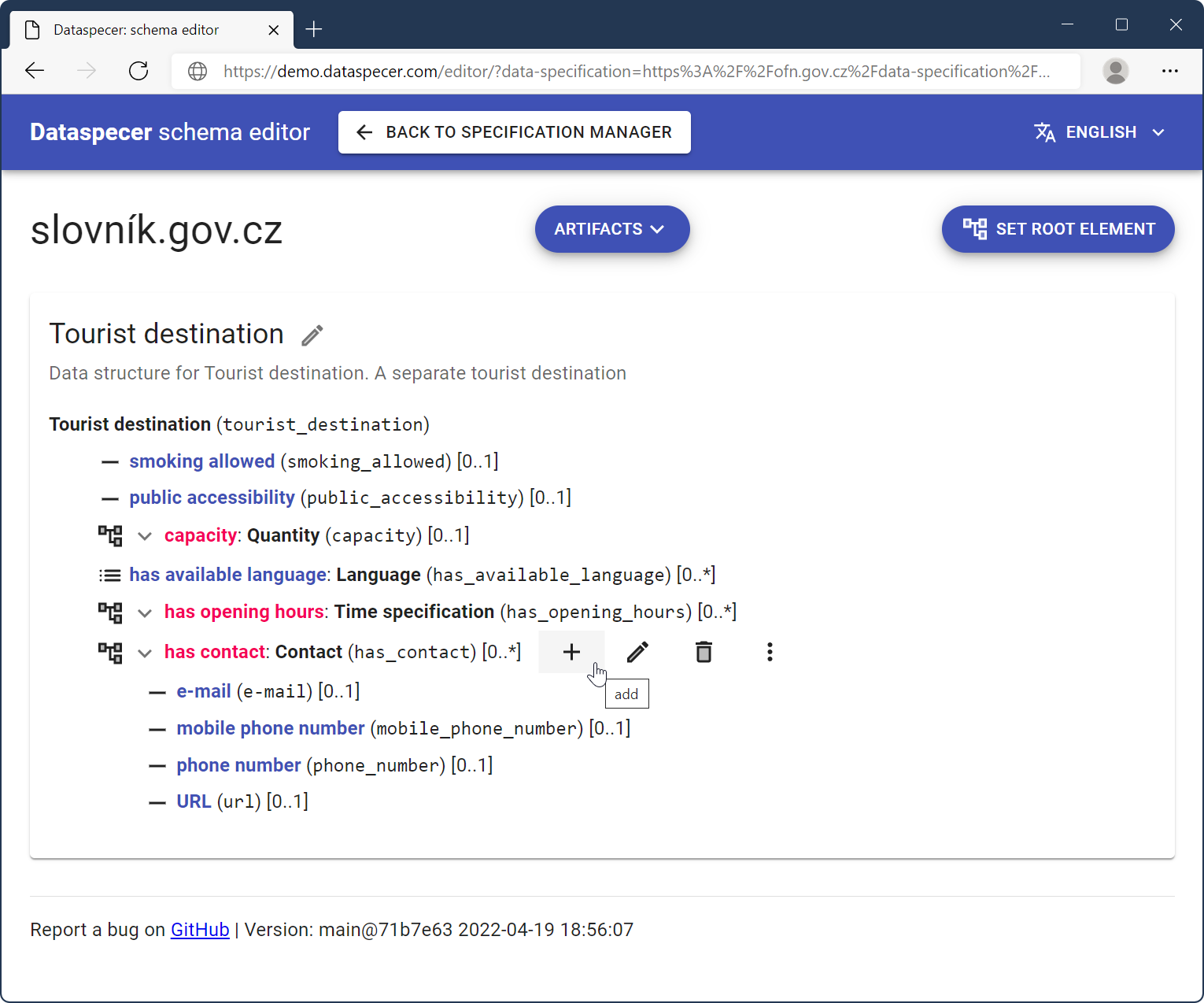
It is also possible to preview the generated schemas right in the editor. Go to “Artifacts” and select a live preview of any data format you want. Although this schema can already be copied and used, we will use specification manager for that.
Go back to the schema manager by clicking on the button in the top left corner or by navigating back in the browser history.
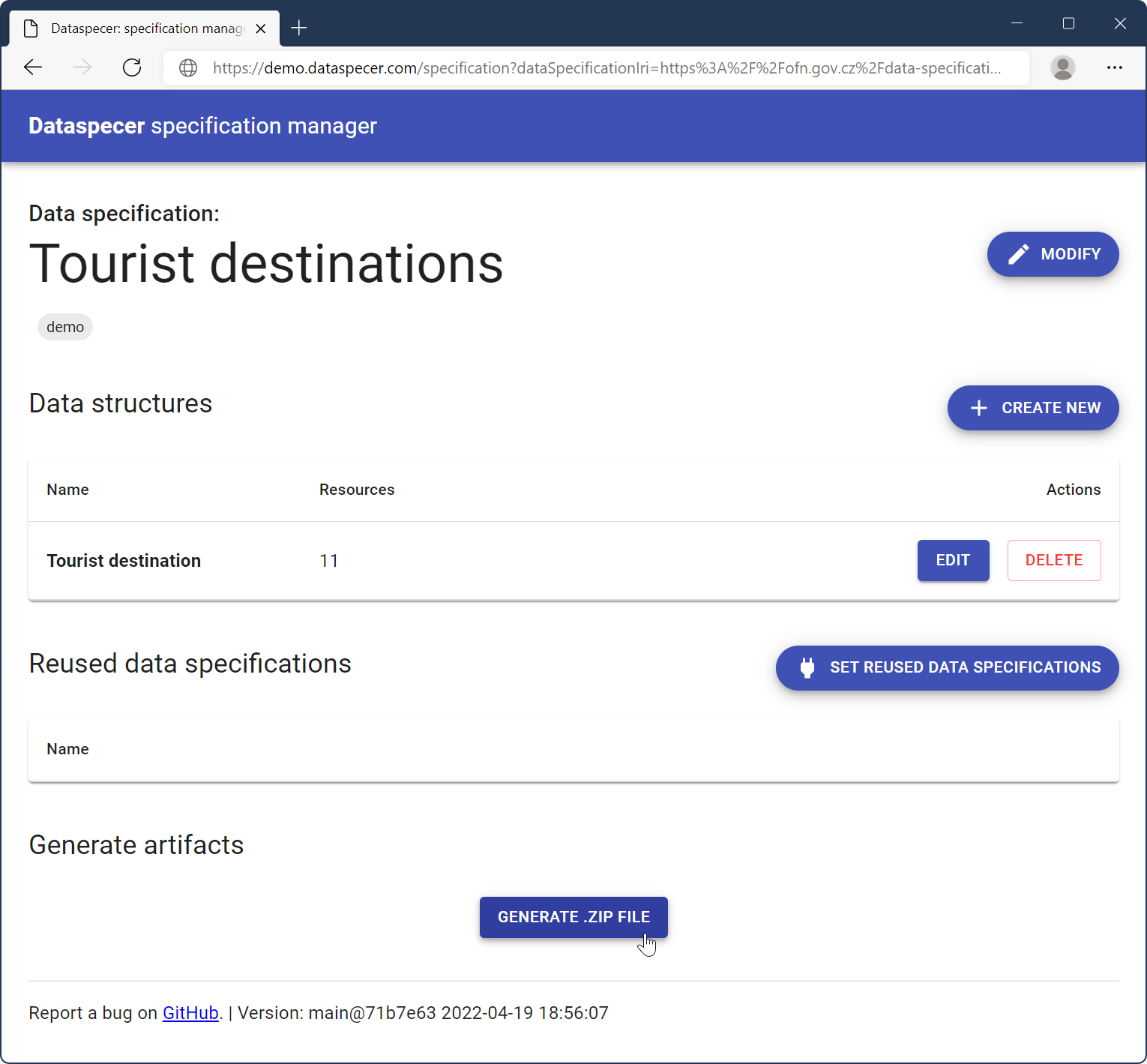
You should see your data structure with the number of resources created. The number represents internal resources, and it is for reference only. In the manager, you may create as many schemas as you want.
When you designed all you wanted to design, click on “Generate .zip file,” which downloads a zip with all data schemas, documentation, and other resources.
Inside, you should find a
bikeshed.htmlfile documenting all the classes used with their attributes and associations, as well as schemas linked, different schema files, and files with internal model data. JSON schema corresponding to our model is shown below.{ "$schema": "https://json-schema.org/draft/2020-12/schema", "title": "Tourist destination", "description": "A separate tourist destination", "type": "object", "required": [], "properties": { "smoking_allowed": { "title": "kouření povoleno", "description": "Určuje, zda je možné v turistickém cíli kouření tabákových výrobků.", "type": "string" }, "public_accessibility": { "title": "public accessibility", "description": "Determines whether a tourist destination is open to the public.", "type": "string" }, "capacity": { "title": "kapacita", "description": "The capacity of a tourist destination, which determines how many visitors the tourist destination can accommodate at one time.", "type": "string", "format": "iri" }, "has_available_language": { "type": "array", "items": { "title": "has available language", "description": "Language available at the location of the tourist facility.", "type": "string", "format": "iri" } }, "has_opening_hours": { "type": "array", "items": { "title": "has opening hours", "description": "Strukturovaná specifikace otevírací doby veřejného místa.", "type": "string", "format": "iri" } }, "has_contact": { "type": "array", "items": { "title": "má kontakt", "description": "Údaje pro kontaktování zástupce veřejného místa, např. provozovatele.", "type": "object", "required": [], "properties": { "e-mail": { "title": "má E-mailovou adresu", "description": "Kontaktní e-mailová adresa.", "type": "string" }, "mobile_phone_number": { "title": "mobile phone number", "description": "Telefonní číslo na mobilní telefon.", "type": "string" }, "phone_number": { "title": "má telefonní číslo na pevnou linku", "description": "Telefonní číslo na pevnou linku.", "type": "string" }, "url": { "title": "URL", "description": "Webová kontaktní adresa: webová stránka či WebID.", "type": "string" } } } } } }